on
CNN Stochastic Gradient Descent
This blog is about a detailed explanation of the Stochastic Gradient Descent of convolutional neural network.
What’s CNN
In deep learning, a convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a class of artificial neural networks (ANN), most commonly applied to analyze visual imagery. (Quoted from Wikipedia)
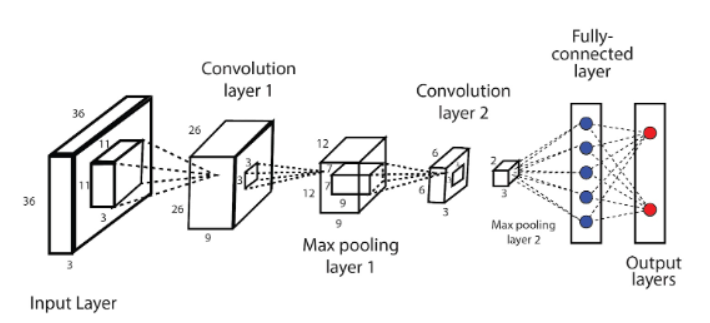 When we use CNN, we often just import torch or import TensorFlow, but if we want to learn more about CNN, we’d better know how the network works and how its parameters are updated. Now, I’ll introduce the complete process of the CNN Stochastic Gradient Descent.
When we use CNN, we often just import torch or import TensorFlow, but if we want to learn more about CNN, we’d better know how the network works and how its parameters are updated. Now, I’ll introduce the complete process of the CNN Stochastic Gradient Descent.
Convolution in DL
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions (f and g) that produces a third function.
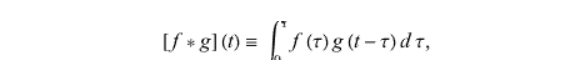 In fact, in deep learning, we instead of convolution operator with cross-correlation.
In fact, in deep learning, we instead of convolution operator with cross-correlation.
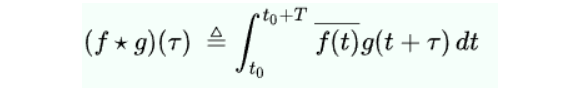 The difference between convolution and cross-correlation is cross-correlation doesn’t content commutative property. That is :
The difference between convolution and cross-correlation is cross-correlation doesn’t content commutative property. That is :
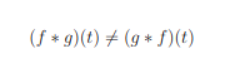 In this article, we don’t distinguish the discrepancy and call the cross-correlation in CNN convolution of machine learning.
In deep learning, we often use a convolutional neural network to matrix-like data like images, etc.
Given an input tensor X=(I, J, K), which stands for a tensor of dimension I×J×K, which I×J matrix stands for an image; a convolutional kernel W=(M, N, K), subject to M far less than I, N far less than J; an output tensor Z=(K, L, K’), where
In this article, we don’t distinguish the discrepancy and call the cross-correlation in CNN convolution of machine learning.
In deep learning, we often use a convolutional neural network to matrix-like data like images, etc.
Given an input tensor X=(I, J, K), which stands for a tensor of dimension I×J×K, which I×J matrix stands for an image; a convolutional kernel W=(M, N, K), subject to M far less than I, N far less than J; an output tensor Z=(K, L, K’), where
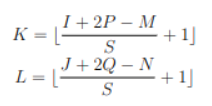 P stands for whether proceeding zero padding or not, S stands for the stride of the convolutional kernel, and K’ stands for the numbers of the convolutional kernel.
P stands for whether proceeding zero padding or not, S stands for the stride of the convolutional kernel, and K’ stands for the numbers of the convolutional kernel.
Convolution Layer Derivative
Assumed the l layer is the convolutional layer and obeys the above definitions.
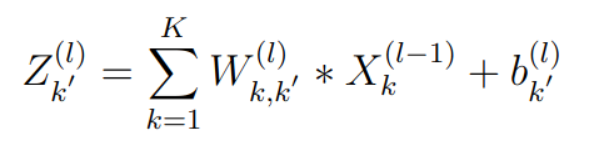 In this formula,* denotes the convolution or to be precise, the cross-correlation, and b denotes the bias vector in the l layer.
We can get the derivative of Z :
In this formula,* denotes the convolution or to be precise, the cross-correlation, and b denotes the bias vector in the l layer.
We can get the derivative of Z :
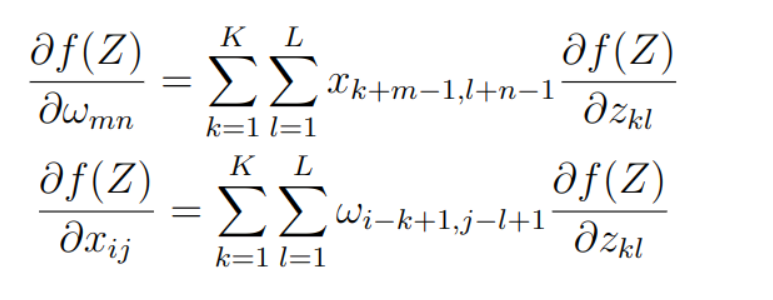 Written as matrices form, we can get this formula:
Written as matrices form, we can get this formula:
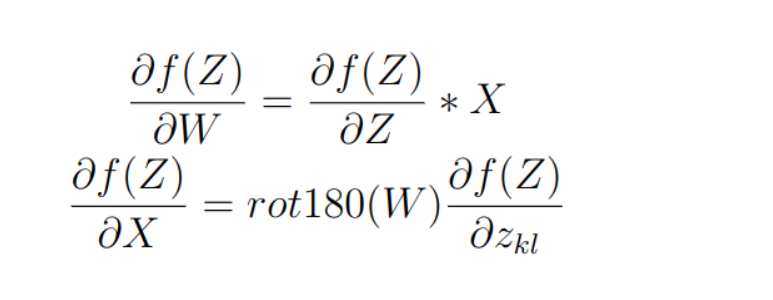 in which rot180 stands for rotating a matrix 180 degrees clockwise, and the start index from the matrix is (1,1) instead of (0,0).In fact ,if we’ve rotated a matrix 180 degrees clockwise ,the new_matrix[i][j]=old_matrix[M+1-i][N+1-j] when the old matrix size is (M,N).
in which rot180 stands for rotating a matrix 180 degrees clockwise, and the start index from the matrix is (1,1) instead of (0,0).In fact ,if we’ve rotated a matrix 180 degrees clockwise ,the new_matrix[i][j]=old_matrix[M+1-i][N+1-j] when the old matrix size is (M,N).
Now let’s recall the architecture of the convolutional layer, in which we input a tensor whose size is (I, J, K), then we use a convolutional kernel tensor (M, N, K’) to scan the input tensor and get an output tensor whose size is (K, L, K’), finally the output tensor will be sent to activation function to become the input tensor of next layer.
we can describe this process by using these formulas:
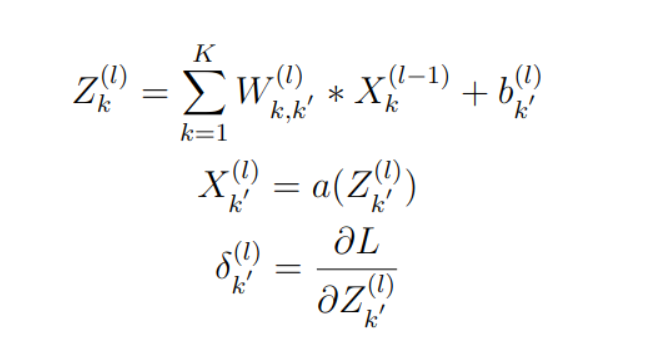 where L means the loss function, we can easily get the derivates of the convolutional layer by the above conclusion:
where L means the loss function, we can easily get the derivates of the convolutional layer by the above conclusion:
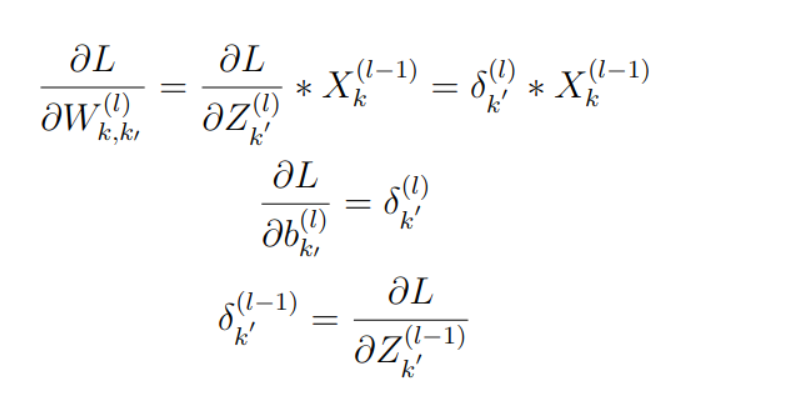 by matrix differential method, we can get :
by matrix differential method, we can get :
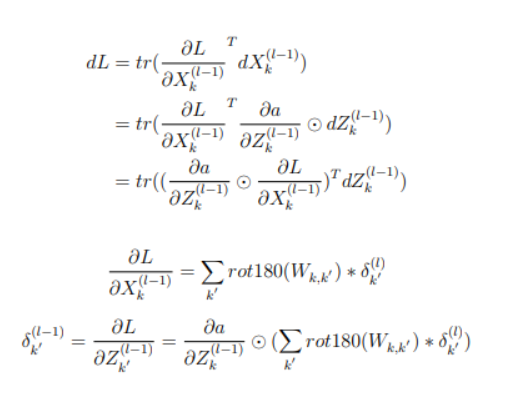 Now, we get the derivatives of the convolutional layer parameters, so we can easily use SGD to optimize our network, the detailed algorithm is shown below:
Now, we get the derivatives of the convolutional layer parameters, so we can easily use SGD to optimize our network, the detailed algorithm is shown below:
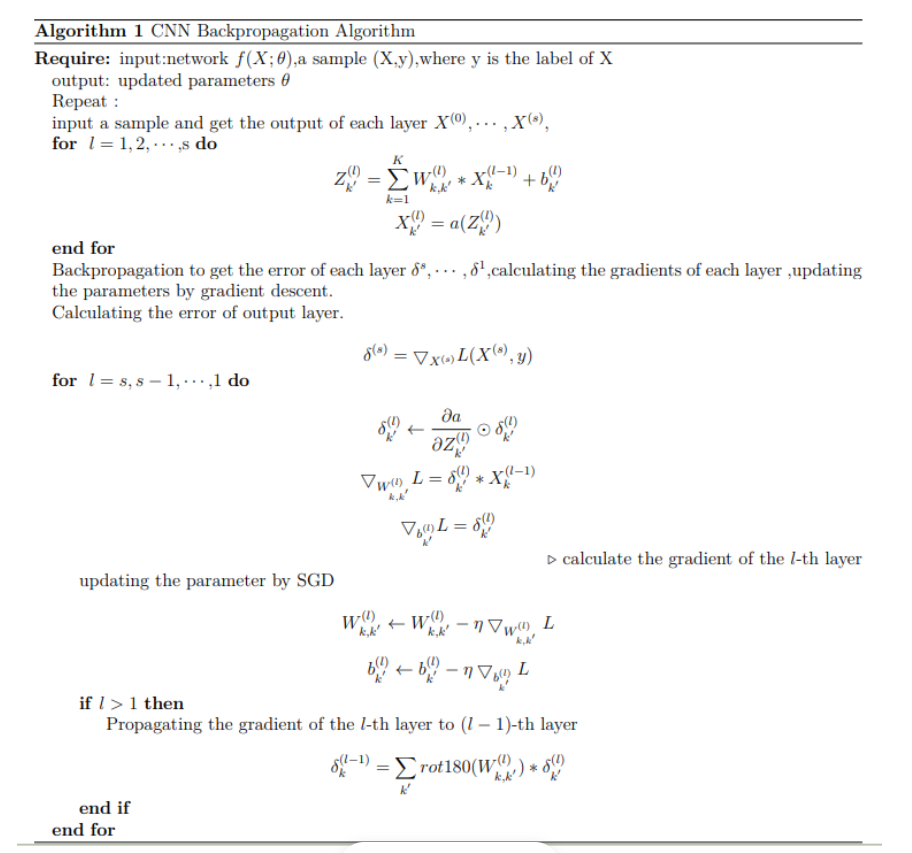
Discussion and feedback